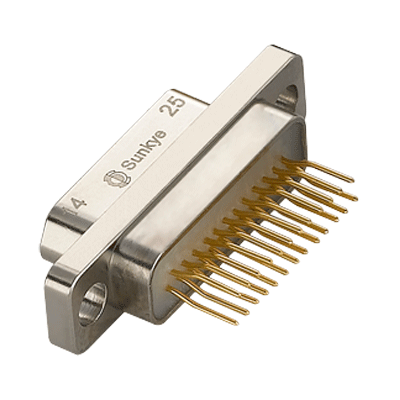
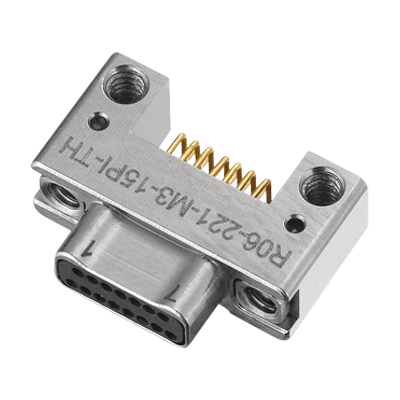
MIL-DTL-83513 Micro D Connectors
MIL-DTL-32139 Nano D Connectors
Discover more applications using Sunkye Connectors' solutions

BNC connectors are very similar to the B and C terminals. A type of threaded connector TNC has better performance than BNC in microwave band.
There are 50 and 75 Ohm versions of the BNC connector. Transmission errors are less likely to occur when 50 Ohm connectors are connected to other impedance cables. Different versions of custom connectors are compatible with each other, but the signal may be reflected if the cable impedance is different. Usually BNC connectors can be used in 4GHz or 2GHz occasions. The 75 Ohm connector is used for the video and DS3 connection to the central offices of telephone companies, while the 50 Ohm connector is used for data and RF transmission. The socket may be damaged if a 50 Ohm plug is improperly connected to a 75 Ohm socket. 75 Ohm connectors are used in VHF applications.
The BNC connector is used for the transmission of radio frequency signals, including the transmission of analog or digital video signals, antenna connections for ham radio equipment and the connection of avionics and other electronic test equipment. In consumer electronics, the BNC connector for video signal transmission has been replaced by RCA terminals, and RCA terminals can be used on devices with only BNC connectors through simple adapters.
BNC terminals have been widely used in 10Base2 Ethernet, and it is difficult to see network cards with BNC terminals because coaxial cables are replaced by twisted pairs. Some ARCNET networks use coaxial cables with BNC terminals.
The BNC connector is suitable for low powered coaxial cables with the bayonet connection mechanism in the frequency range of 0-4GHz. This kind of connector can be quickly connected and separated, and it has reliable connection, good vibration resistance as well as convenient connection and separation, which is suitable for occasions that require frequent connections and separations. It is widely used to connect coaxial radio frequency cables in radio equipment and test instruments.
The characteristic impedance is very important, otherwise it will cause mismatching. When the impedance matches the military style electrical connectors, the maximum output power can be obtained and the equipment utilization efficiency is the highest. When the impedance does not match the connector, the effective output power will decrease. An impedance matching can be realized when the external impedance is equal to the internal impedance of the device.
The BNC connector must be connected to both ends of each cable segment. The BNC cable connector consists of a central pin, a jacket and a booth. It includes three parts: the BNC connector base, the jacket and the probe. The BNC connector was named according to the way it locks and its inventors Paul Neal of Bell Laboratory (who invented the N-terminal) and Carl Conseiman of Amphenol Corporation (who invented the C-terminal).
The NC connector is very similar to the B and C terminals. A type of connector TNC(Threaded Neill-Concelman) has better performance than BNC in microwave band.
The BNC connector is used for the transmission of radio frequency signals, including the transmission of analog or digital video signals, antenna connections for ham radio equipment and the connection of avionics and other electronic test equipment.
In consumer electronics, the BNC connector for video signal transmission has been replaced by the RCA terminals, and RCA terminals can be used on devices with only BNC connectors through simple adapters. BNC terminals have been widely used in 10Base2 Ethernet, and it is difficult to see network cards with BNC terminals because coaxial cables are replaced by twisted pairs. Some ARCNET networks use coaxial cables with BNC terminals.
Main characteristics of BNC:
1. The characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance of 50Ω and 75Ω are used mostly in the BNC RF connector. Many series connectors have the specifications of 50Ω and 75Ω at the same time. In general, 50Ωconnectors are used in products with high frequency and high performance; 75Ω connectors are used in products with lower frequency, and the frequency is usually under 4 GHZ. Particularly, consumer electronics videos adopt 75Ω connectors more. Uses should select connectors that match the impedance of their own products. For example, a 75 Ω connector should be selected if the user is using a 75Ω RG 59 Cable.
2. The frequency
Each RF connector has a use frequency range, and users need to know the operating frequencies of their own products when selecting connectors. The connector frequency that is below the required operating frequency will affect the electrical performance of the whole machine, or choosing expensive high-precision and high-frequency connectors can be wasteful. It should be noted that the use frequency of connectors designed by different companies is quite different, and the use frequency of inferior products is far from meeting industry requirements. Therefore, users should confirm the electrical perf
ormance description of the product when selecting connectors.
3. VSWR
VSWR is one of the most important performance indicators of mil spec RF connectors and a measurement standard of the signal amount that returns from the connector. It is a vector unit including the amplitude and phase components. The VSWR of connectors of the same model is different at different frequencies. In general, the VSWR increases with the increase of the operating frequency. Users can enquire the manufacturer if they want to know the VWSR at a particular frequency of the connector.
Sunkye Connection Technologies provides a wide product portfolio with a complete interconnect solutions offering. Sunkye connectors and cables assemblies are complementary with Sunkye backshells and conduits.
 Jun 21, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (2)
Jun 21, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (2)
 Aug 09, 2019
Development of Micro Connector
Aug 09, 2019
Development of Micro Connector
 Jun 06, 2019
Alloy 52 UNS N14052 Material Report
Jun 06, 2019
Alloy 52 UNS N14052 Material Report
 Apr 28, 2020
How to Detect Medical Connectors
Apr 28, 2020
How to Detect Medical Connectors
 May 31, 2019
TWIST PIN: THE LIGHTSPOT OF SUNKYE
May 31, 2019
TWIST PIN: THE LIGHTSPOT OF SUNKYE
 Nov 14, 2019
How To Choose The Right Connector
Nov 14, 2019
How To Choose The Right Connector
 Sep 24, 2019
Notes for Welding D Type Connector
Sep 24, 2019
Notes for Welding D Type Connector
 May 10, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (1)
May 10, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (1)
 Jan 16, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Strip Connector
Jan 16, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Strip Connector
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye at Expo Electronica 2014, Moscow
May 31, 2019
Sunkye at Expo Electronica 2014, Moscow
 Jan 28, 2020
The Connector Industry Is Booming
Jan 28, 2020
The Connector Industry Is Booming
 Dec 08, 2019
Connection Methods Of The Connector
Dec 08, 2019
Connection Methods Of The Connector
 Jan 22, 2020
Differences Between Connector And Terminal
Jan 22, 2020
Differences Between Connector And Terminal
 Aug 07, 2019
A Revolution in Connector Technology
Aug 07, 2019
A Revolution in Connector Technology
 Nov 02, 2021
MEET SUNKYE AT SAHA EXPO 2021 FAIR!
Nov 02, 2021
MEET SUNKYE AT SAHA EXPO 2021 FAIR!
 Oct 20, 2020
The Failure Mechanism of Connectors
Oct 20, 2020
The Failure Mechanism of Connectors
 Oct 30, 2019
D Sub Connector Introduction
Oct 30, 2019
D Sub Connector Introduction
 Jan 01, 2020
Development Trend Of Automobile Connector In China
Jan 01, 2020
Development Trend Of Automobile Connector In China
 Feb 19, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors
Feb 19, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Features of Type C
May 31, 2019
Features of Type C
 Jul 18, 2020
The Basic Structure of the Connector
Jul 18, 2020
The Basic Structure of the Connector
 May 27, 2021
The Importance of Connectors in Electrical Equipment
May 27, 2021
The Importance of Connectors in Electrical Equipment
 Oct 02, 2023
MEET SUNKYE AT ADIPEC 2023 FAIR
Oct 02, 2023
MEET SUNKYE AT ADIPEC 2023 FAIR
 May 04, 2020
Automotive Connectors
May 04, 2020
Automotive Connectors
 Dec 08, 2020
Some Knowledge about RJ45 Connector
Dec 08, 2020
Some Knowledge about RJ45 Connector
 Oct 01, 2020
Structure and Material of Waterproof Connector
Oct 01, 2020
Structure and Material of Waterproof Connector
 Jan 03, 2024
Connector — A Big Player in Your Supply Chain
Jan 03, 2024
Connector — A Big Player in Your Supply Chain
 Jun 12, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (1)
Jun 12, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (1)
 Dec 23, 2019
Technical Principles Of Connectors
Dec 23, 2019
Technical Principles Of Connectors
 Jul 08, 2021
Structural Analysis of Aerospace Connector
Jul 08, 2021
Structural Analysis of Aerospace Connector
 Aug 01, 2022
Connectors Make Sensors Work Well on Equipment
Aug 01, 2022
Connectors Make Sensors Work Well on Equipment
 Nov 03, 2019
Some Solutions For Poor Terminal Pressing
Nov 03, 2019
Some Solutions For Poor Terminal Pressing
 Nov 15, 2019
How To Make High-Quality Connector
Nov 15, 2019
How To Make High-Quality Connector
 Jan 04, 2021
The Structure and Material of Connectors
Jan 04, 2021
The Structure and Material of Connectors
 Jul 03, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (1)
Jul 03, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (1)
 Sep 08, 2022
How Does Environment Temperature Affect Connectors?
Sep 08, 2022
How Does Environment Temperature Affect Connectors?
 Jul 15, 2020
Classification of Connectors
Jul 15, 2020
Classification of Connectors
 Dec 26, 2019
How To Classify Industrial Connectors
Dec 26, 2019
How To Classify Industrial Connectors
 Oct 07, 2020
How to Distinguish FFC Connector and FPC Connector
Oct 07, 2020
How to Distinguish FFC Connector and FPC Connector
 Sep 08, 2019
What are Avionics Connectors?
Sep 08, 2019
What are Avionics Connectors?
 Jan 18, 2021
Knowledge of FPC Connectors
Jan 18, 2021
Knowledge of FPC Connectors
 Jul 09, 2020
The Importance of Connectors in Medical Equipment
Jul 09, 2020
The Importance of Connectors in Medical Equipment
 Nov 11, 2019
Brief Introduction Of Automobile Connector
Nov 11, 2019
Brief Introduction Of Automobile Connector
 Mar 29, 2020
Demand for Heavy Truck Connectors Increases
Mar 29, 2020
Demand for Heavy Truck Connectors Increases
 Nov 01, 2021
Meet Sunkye at SEDEC 2020 Fair!
Nov 01, 2021
Meet Sunkye at SEDEC 2020 Fair!
 Apr 22, 2020
Production Process of Connector Contacts
Apr 22, 2020
Production Process of Connector Contacts
 Sep 14, 2019
Miniaturization Trend of Mil Connectors
Sep 14, 2019
Miniaturization Trend of Mil Connectors
 May 13, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (2)
May 13, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (2)
 Jan 04, 2023
Four Connection Methods of Circular Connectors
Jan 04, 2023
Four Connection Methods of Circular Connectors
 Nov 09, 2019
Introduction To Connector Knowledge
Nov 09, 2019
Introduction To Connector Knowledge
 Jul 12, 2020
Introduction to the Connector
Jul 12, 2020
Introduction to the Connector
 Oct 06, 2020
Description of Pogo Pin Connectors
Oct 06, 2020
Description of Pogo Pin Connectors
 Nov 12, 2019
Production Technology of Connector
Nov 12, 2019
Production Technology of Connector
 Dec 29, 2019
Material Of Automotive Connectors
Dec 29, 2019
Material Of Automotive Connectors
 Sep 13, 2020
Fusion of Connectors and Sensors
Sep 13, 2020
Fusion of Connectors and Sensors
 Apr 25, 2020
The Second Generation Circular Military Connector
Apr 25, 2020
The Second Generation Circular Military Connector
 Jan 11, 2021
How to Select Connectors for Hardware Design
Jan 11, 2021
How to Select Connectors for Hardware Design
 Jan 25, 2021
The Analysis of Connector Electroplating Problems
Jan 25, 2021
The Analysis of Connector Electroplating Problems
 Sep 04, 2019
Market Profile of Micro PCB Connectors
Sep 04, 2019
Market Profile of Micro PCB Connectors
 Mar 20, 2020
Connector Quality Test Type
Mar 20, 2020
Connector Quality Test Type
 May 31, 2019
SUNKYE will Release Type C Project on October
May 31, 2019
SUNKYE will Release Type C Project on October
 Oct 06, 2019
How Military Spec Connectors Work
Oct 06, 2019
How Military Spec Connectors Work
 Oct 13, 2020
Various Coaxial Connectors
Oct 13, 2020
Various Coaxial Connectors
 Oct 18, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
Oct 18, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
 Aug 02, 2021
Introduction to Vehicle Connectors
Aug 02, 2021
Introduction to Vehicle Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Connector
May 31, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Connector
 Sep 20, 2019
Strictness of Military/Aerospace Specifications
Sep 20, 2019
Strictness of Military/Aerospace Specifications
 Sep 28, 2019
Development Trend of Miniature Connectors Technology
Sep 28, 2019
Development Trend of Miniature Connectors Technology
 Nov 05, 2019
Wearable Connectors Tend to be Miniaturization
Nov 05, 2019
Wearable Connectors Tend to be Miniaturization
 Jan 07, 2020
The Performance Of Automobile Connector
Jan 07, 2020
The Performance Of Automobile Connector
 Nov 06, 2019
Connector Classification
Nov 06, 2019
Connector Classification
 Oct 31, 2019
The Introduction Of SMT
Oct 31, 2019
The Introduction Of SMT
 Mar 08, 2020
Sunkye: Safety, Innovation, Reliability
Mar 08, 2020
Sunkye: Safety, Innovation, Reliability
 Jul 21, 2020
What is a Military Specification Circular Connector?
Jul 21, 2020
What is a Military Specification Circular Connector?
 Apr 01, 2020
Connectors for Special Applications
Apr 01, 2020
Connectors for Special Applications
 Jun 18, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (1)
Jun 18, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (1)
 Dec 22, 2020
The Transient Interruption Detection of Connectors
Dec 22, 2020
The Transient Interruption Detection of Connectors
 Jun 25, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Datasheet
Jun 25, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Datasheet
 Sep 06, 2019
Polytetrafluoroethylene-PTFE
Sep 06, 2019
Polytetrafluoroethylene-PTFE
 Jun 15, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (2)
Jun 15, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (2)
 Jun 01, 2021
Functions and Advantages of Electrical Connectors
Jun 01, 2021
Functions and Advantages of Electrical Connectors
 Jul 06, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (2)
Jul 06, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (2)
 Jul 17, 2020
Sunkye Market Matrix
Jul 17, 2020
Sunkye Market Matrix
 Feb 25, 2020
How to Choose the Right Medical Connector
Feb 25, 2020
How to Choose the Right Medical Connector
 Sep 19, 2020
The Necessity of Waterproof Connectors
Sep 19, 2020
The Necessity of Waterproof Connectors
 Sep 25, 2020
Related Knowledge of SMA RF Connector
Sep 25, 2020
Related Knowledge of SMA RF Connector
 Nov 04, 2019
How Military Connectors Work
Nov 04, 2019
How Military Connectors Work
 Jun 27, 2020
Crimping and Welding of Military Connectors
Jun 27, 2020
Crimping and Welding of Military Connectors
 Dec 17, 2019
Interconnection Level Of Connector
Dec 17, 2019
Interconnection Level Of Connector
 Dec 01, 2021
Connectors' Revolution of 1000km off The Earth
Dec 01, 2021
Connectors' Revolution of 1000km off The Earth
 Nov 10, 2020
The Manufacturing Process of Electronic Connectors
Nov 10, 2020
The Manufacturing Process of Electronic Connectors
 Nov 23, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
Nov 23, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
 Oct 13, 2023
Several Design Ideas for Electronic Connectors
Oct 13, 2023
Several Design Ideas for Electronic Connectors
 Aug 15, 2023
Extreme Conditions Bring up Hermetic Connectors
Aug 15, 2023
Extreme Conditions Bring up Hermetic Connectors
 Sep 28, 2021
Correct Use and Safety of Avionics Connectors
Sep 28, 2021
Correct Use and Safety of Avionics Connectors
 Nov 10, 2019
The Future Trend Of Automobile Connector
Nov 10, 2019
The Future Trend Of Automobile Connector
 Nov 08, 2019
Miniaturization Development Technology Of Connector
Nov 08, 2019
Miniaturization Development Technology Of Connector
 Nov 01, 2019
Five Common Features of USB Connector
Nov 01, 2019
Five Common Features of USB Connector
 Nov 29, 2019
Importance Of Connectors
Nov 29, 2019
Importance Of Connectors
 Sep 12, 2019
Reliable Connectors Are the Secret of UAV Success
Sep 12, 2019
Reliable Connectors Are the Secret of UAV Success
 Nov 17, 2020
Selection Factors for SMA Connectors
Nov 17, 2020
Selection Factors for SMA Connectors
 Dec 01, 2020
How to Improve the Reliability of RF Connectors
Dec 01, 2020
How to Improve the Reliability of RF Connectors
 Jun 24, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (3)
Jun 24, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (3)
 Oct 10, 2019
Types and Advantages of D-sub Connectors
Oct 10, 2019
Types and Advantages of D-sub Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Everything You Need to Know: Type C
May 31, 2019
Everything You Need to Know: Type C
 Feb 07, 2020
The Rapidly Growing Market For Medical Connectors
Feb 07, 2020
The Rapidly Growing Market For Medical Connectors
 Nov 24, 2019
The Connector Applications Are Everywhere
Nov 24, 2019
The Connector Applications Are Everywhere
 Jul 30, 2019
Market Status of Micro Connectors
Jul 30, 2019
Market Status of Micro Connectors
 Apr 04, 2020
The Material of the Connector
Apr 04, 2020
The Material of the Connector
 Aug 09, 2021
What Are High Density Connectors?
Aug 09, 2021
What Are High Density Connectors?
 Sep 18, 2019
Definition of Mil Standard Connector
Sep 18, 2019
Definition of Mil Standard Connector
 Aug 02, 2020
Electrical Performance of Connector
Aug 02, 2020
Electrical Performance of Connector
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye Will Postpone the Release of USB 3.1 Type C
May 31, 2019
Sunkye Will Postpone the Release of USB 3.1 Type C
 Dec 05, 2019
Disassembly Tools For Automotive Connectors
Dec 05, 2019
Disassembly Tools For Automotive Connectors
 Dec 11, 2019
The Main Classification Of Crimp Connection
Dec 11, 2019
The Main Classification Of Crimp Connection
 Feb 10, 2020
The Function And Prospect Of Medical Connector
Feb 10, 2020
The Function And Prospect Of Medical Connector
 Nov 17, 2023
Future Development Trends of Circular Connectors
Nov 17, 2023
Future Development Trends of Circular Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye Type C 10Gbps Test on April
May 31, 2019
Sunkye Type C 10Gbps Test on April
 Nov 03, 2020
The Guide for Selecting Electrical Connectors
Nov 03, 2020
The Guide for Selecting Electrical Connectors
 Apr 13, 2020
Why is a Poor Connector Prone to Fire?
Apr 13, 2020
Why is a Poor Connector Prone to Fire?
 Jan 31, 2020
The Development Of D-sub Connectors
Jan 31, 2020
The Development Of D-sub Connectors
 Feb 13, 2020
Connection Between Brain And Machine
Feb 13, 2020
Connection Between Brain And Machine
 Sep 21, 2021
Connection Mode and Purchase of Aerospace Connector
Sep 21, 2021
Connection Mode and Purchase of Aerospace Connector
 Feb 15, 2021
The Power Capacity of RF Coaxial Connectors
Feb 15, 2021
The Power Capacity of RF Coaxial Connectors
 Jan 13, 2020
Overall Performance Parameters Of Connector
Jan 13, 2020
Overall Performance Parameters Of Connector
 Aug 03, 2019
Connector D Type
Aug 03, 2019
Connector D Type
 Jan 19, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Flat Cable Connector
Jan 19, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Flat Cable Connector
 Jan 25, 2020
Four Types Of Industrial Electrical Connectors
Jan 25, 2020
Four Types Of Industrial Electrical Connectors
 Feb 08, 2021
Four Attention Points in Using Power Connectors
Feb 08, 2021
Four Attention Points in Using Power Connectors
 Apr 07, 2020
Market Status of Miniature Connectors
Apr 07, 2020
Market Status of Miniature Connectors
 Sep 26, 2019
Market Status of Micro Miniature Connectors
Sep 26, 2019
Market Status of Micro Miniature Connectors
 Nov 17, 2022
Robotic Arm Works 7*24 in Manufacturing
Nov 17, 2022
Robotic Arm Works 7*24 in Manufacturing
 Sep 02, 2019
Four Processes of Producing Connectors
Sep 02, 2019
Four Processes of Producing Connectors
 Dec 14, 2019
Naming Of Connectors
Dec 14, 2019
Naming Of Connectors
 Oct 13, 2020
Selection Factors of RF Connectors
Oct 13, 2020
Selection Factors of RF Connectors
 Dec 02, 2019
Basic Structural Member Of Connector
Dec 02, 2019
Basic Structural Member Of Connector
 Oct 19, 2021
Subsea Connector needs a new revolution
Oct 19, 2021
Subsea Connector needs a new revolution
GET IN TOUCH
MIL-DTL-32139 Nano D Connectors
 English
English  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  Türkçe
Türkçe  Svenska
Svenska  Nederland
Nederland